Incident Response: Third-Party Breach
Here are the key takeaways from this blog: Vendor trust isn't security—verify everything. Embed cybersecurity requirements into contracts, conduct...

Cyber threats are accelerating, making proactive, well-tested incident response programs essential as regulators demand documented and practiced readiness. Organizations that combine preparation, automation, and regular exercises are better equipped to reduce response time, close operational gaps, and limit business impact.
Key takeaways from this article:
Download Rivals Free Incident Response Template
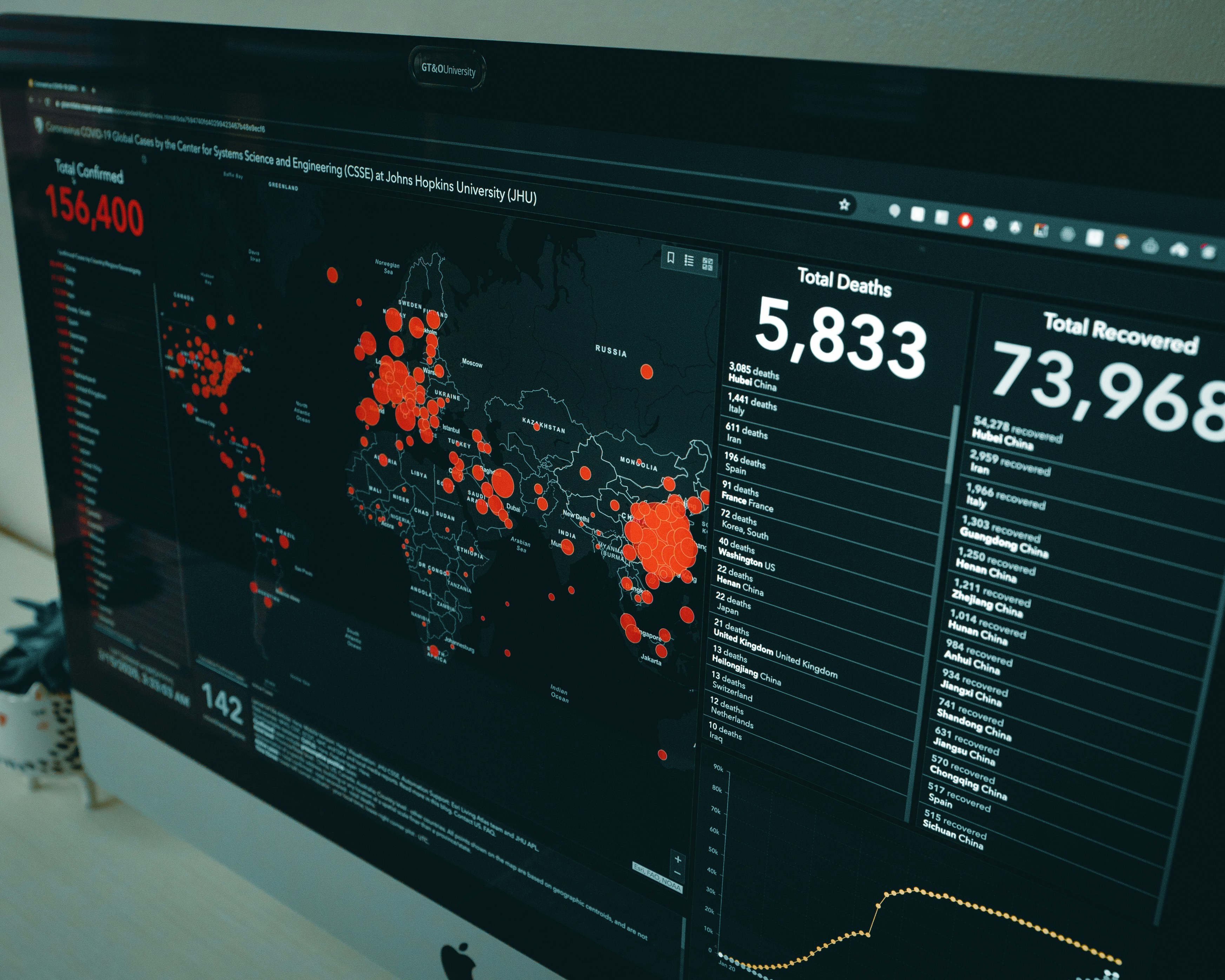
The risk isn’t just evolving, it’s accelerating. In 2025, ransomware crews like Qilin, Scattered Spider, SafePay, and Akira rolled out zero-day techniques that shredded legacy defenses and exposed gaps even in well-funded security programs. Their targets weren’t random; they went straight after the backbone of global business like financial services, cloud platforms, and critical supply chains. Each new campaign demonstrates how fast adversaries are learning, sharing tools, and scaling operations, turning isolated breaches into multi-million-dollar disruptions felt across industries.
The April 2025 release of NIST SP 800-61 Rev 3, aligned with CSF 2.0, raised the floor for incident readiness, with regulators now demanding detailed documentation, evidence of practice, and rapid reporting. Combined with requirements from GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS v4.0, the message is clear: a written plan sitting on a shelf is no longer acceptable. Breaches are no longer just IT problems; they halt operations, drain revenue, and erode customer trust, with reputational fallout escalating when stolen data is posted online. In July 2025, for example, SafePay claimed to have exfiltrated 3.5 TB of Ingram Micro data through stolen VPN credentials, an attack that disrupted global distribution pipelines and shook confidence across its partner ecosystem.
Strong incident response isn’t just about having a binder full of plans—it’s about ensuring the organization can act with speed, consistency, and confidence under pressure. Standardized playbooks for ransomware, phishing, insider threats, and cloud breaches create that consistency, eliminating the hesitation that costs precious minutes.
Automation takes it further. By using SOAR platforms and AI-driven triage, teams can drastically cut false positives and reduce mean time to respond, freeing analysts to focus on judgment-driven decisions instead of routine tasks. But technology alone won’t carry the day. Regular exercises, monthly phishing campaigns, and full-scope simulations twice a year—force teams to think and act under real-world conditions, sharpening instincts in ways dashboards never can.
The value of threat intelligence comes into play here as well. Correlating alerts with CVEs, MITRE ATT&CK techniques, and geolocation data accelerates containment and helps leaders understand the “who” and “how” behind an incident. Executive engagement is another critical ingredient; quarterly briefings that tie IR metrics like MTTD and MTTR directly to revenue impact and regulatory risk keep leadership aligned and supportive.
Finally, in today’s perimeterless environment, effective incident response must extend beyond the walls of the organization. SaaS providers, IaaS platforms, and critical vendors all need to be part of the playbooks, the notification SLAs, and the tabletop drills—because a chain is only as strong as its weakest link.
Even the most mature incident response programs run into friction points that can erode effectiveness. Five challenges stand out in particular—and each has clear remedies.
Alert Fatigue is at the top of the list. Security teams often drown in thousands of daily alerts, many of which are false positives. The result: analyst burnout and missed signals. The fix lies in smarter tuning—refining detection rules, integrating contextual enrichment, and letting AI-driven correlation engines prioritize the alerts that actually matter. By filtering noise at the source, teams can focus on the 5% of events that truly need human attention.
Skill Gaps are another persistent issue. IR requires a blend of technical depth, investigative instincts, and cross-team coordination skills, but those capabilities are scarce. Forward-leaning organizations invest in IR-specific career paths, fund certifications like GCIH or GCFA, and run internal training labs. When internal coverage can’t keep pace, managed detection and response (MDR) providers can bridge the gap, giving teams breathing room while internal talent matures.
Siloed Data can cripple investigations. Logs scattered across endpoints, firewalls, SaaS platforms, and cloud providers slow analysts down and lead to blind spots. Centralizing evidence into a single data lake—and connecting tools through APIs—creates a unified flow of context. That integration shortens investigation timelines and ensures nothing slips between cracks.
Cloud Blind Spots are becoming even more dangerous as workloads move to IaaS and SaaS environments. Without robust logging, activity in the cloud can be invisible until it’s too late. Enabling cloud-trail logging, layering on Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM), and leveraging Security Service Edge (SSE) platforms restore end-to-end visibility and allow teams to apply the same rigor to cloud incidents as they do on-premises.
Post-Mortem Apathy often undermines long-term resilience. After a crisis subsides, teams are tempted to “move on” without fully learning from what happened. A disciplined approach requires root cause analysis (RCA) within five business days, documented lessons learned, and enforced closure of remediation tasks through the ticketing system. Without accountability, the same gaps are likely to resurface in the next breach.
Building an effective incident response program doesn’t have to be overwhelming. With guided templates and scenario playbooks, our platform helps you capture the right people, policies, and processes while ensuring your plan stays exam-ready. You can then put that plan to the test through tailored exercises that tie directly into your teams, audit findings, and security posture improvements.
And when a real incident occurs, the platform shifts from planning to action. Checklists walk your team step by step through the response, while prioritized action items ensure nothing slips through the cracks. The result: a response program that’s not only documented, but truly actionable when it matters most.
Download Rivals Free Incident Response Template
Here are the key takeaways from this blog: Vendor trust isn't security—verify everything. Embed cybersecurity requirements into contracts, conduct...

1 min read
Here are the key takeaways from this blog: Ransomware attacks are more sophisticated and costly than ever, with 2023 payouts exceeding $1 billion...

In the world of cybersecurity, incident response management is a critical component of protecting your organization's data. When an incident occurs,...