Incident Response: Third-Party Breach
Here are the key takeaways from this blog: Vendor trust isn't security—verify everything. Embed cybersecurity requirements into contracts, conduct...

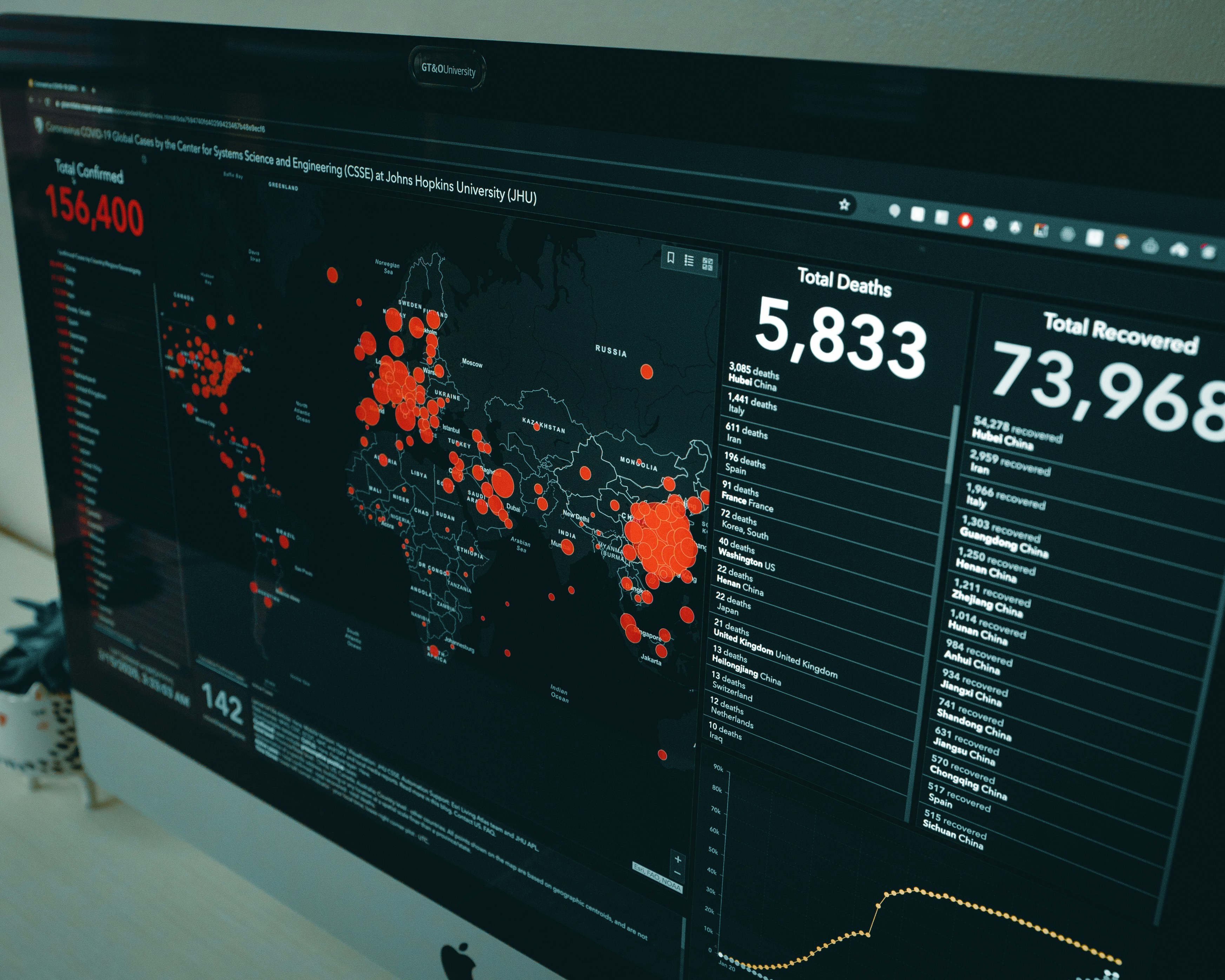
In the event of a cybersecurity incident, time is of the essence. You likely know that keeping security top of mind is critical for organizations, and that security measures contribute to the safety of both the business and the personnel that staff and support it. But, what happens in the event of a breach? Regardless of your company’s size, you need to have incident response steps in place to ensure that you take proactive rather than reactive action to stop the breach in its tracks, and to quickly and efficiently deal with any fallout that can occur as a result of the occurrence.
In today's world, where technology advances each day, cyber threats are rising and many companies risk losing sensitive information to cybercriminals. That's why it is vital to set up a plan to guide you in implementing security measures to safeguard your organization.
CSO Online defines incident response (IR) as “how an organization responds to a data breach or cyberattack.” A cybersecurity incident response plan is a structured outline, prepared in advance, that guides an organization in implementing security protocols as well as the proper steps to take if breaches and cyber threats were to occur. The plan also enables the company to identify the root cause of security concerns and find possible solutions to mitigate situations if they happen before it is too late.
When your organization is under attack, it can quickly become challenging to deal with, but when every second counts, a slow response can be that much more costly than if you’d had a plan to stop it and manage it fast. Avoiding bad decisions that happen in a last-minute rush is perhaps the biggest benefit of having incident response steps at the ready.
When you start preparing before a threat is made real, it is much easier to deal with if and when it happens. This includes putting systems and personnel in place to ensure an effective response to security incidents. For example, you can train your employees on security response protocols and strategies ahead of time. Share proper actions to take in the event of a data breach from the smallest incident to a full scale attack.
Create and write down all of the policies and procedures that your team will need to use as a guide following each type of incident. Include things like - what to do if an employee clicks a malicious link or how to handle phishing emails. Don’t forget to include contact information for critical personnel to reach out to in a security incident, and provide written guidelines of responsibilities for each team member. This will help your team members know what is expected of them so everyone can operate appropriately.
It’s not a bad idea to create training courses that you regularly implement quarterly too. Whether employees or new or have been around a while, these courses will ensure everyone knows the best course of action for all potential threats. Drills may help drive the point home for your team as well.
This is the phase of incident response steps we hope you never need because it means a breach has occurred. At this point you need to ask what the cause or source of the cyber threat that resulted in a breach was. Collect as much data as possible during this process to analyze how the breach occurred in the first place, and if it could be prevented from happening again. Your team will need to report the following:
These reports should be written as soon as possible while memories are fresh. Then, they should be thoroughly analyzed as this information can be used to potentially prevent future cyber incidents. If nothing else, these reports can help you come up with a way to respond to future incidents faster.
Once you encounter a cyberattack or data breach, resist the urge to delete anything as it can make matters worse, and you could be destroying crucial data that can help to mitigate the current situation and prevent future issues. Instead, focus on containing the breach to prevent it from spreading further.
Note: Keep all team members apprised of what’s going on every step of the way - especially if you will be shutting down a system that could impact them directly. For example, shutting down the payroll systems to prevent a loss of funding that could result in a delay in employees getting paid. The more informed your team is, the better. It’s also a good idea to let employees know as soon as possible if you need them to change passwords, and alter their current methods of communication (i.e. only making phone calls in lieu of sending email correspondence for them time being).
At this point, your goal is to remove the threat completely from your systems. It might take longer if the threat has moved through multiple areas. That’s why swift containment is crucial. Eradication may require things like malware scanning and removal, deleting websites and uploading backups, sweeping for other viruses, wiping computers/systems, and more.
Now, you’ll work to get everything back online and get your systems functional again in the hopes of going back to business as usual. However, you will also need to begin the work of assessing the damages caused by the incident. Remember, document everything along the way. Not only will this help you prevent future attacks, but these reports may be needed in the event of legal proceedings that could follow from the attack.
The dust is beginning to settle, but the work isn’t quite done yet. Now, take all of the reports and analyses to reassess your security protocols. Use the lessons learned to better fortify your organization and prevent future attacks. Once you’ve created new safety measures go back to step one, retrain your team, and hopefully you won’t have to use steps two through six again.
Contact Rivial Security for a cybersecurity risk assessment for your organization today.
Here are the key takeaways from this blog: Vendor trust isn't security—verify everything. Embed cybersecurity requirements into contracts, conduct...

1 min read
Here are the key takeaways from this blog: Know the Regulatory Definitions and Deadlines — NCUA and FDIC have strict criteria and timelines (72 and...

1 min read
Here are the key takeaways from this blog: Ransomware attacks are more sophisticated and costly than ever, with 2023 payouts exceeding $1 billion...